 Google initiates more than 400,000 manual actions every month, according to Matt Cutts, the head of Google’s webspam team. Concurrently, Google processes 20,000 reconsideration requests in that same time period. Since a percentage of these reconsideration requests aren’t first timers, less than one reconsideration request is processed for every 20 penalties.
Google initiates more than 400,000 manual actions every month, according to Matt Cutts, the head of Google’s webspam team. Concurrently, Google processes 20,000 reconsideration requests in that same time period. Since a percentage of these reconsideration requests aren’t first timers, less than one reconsideration request is processed for every 20 penalties.
In my experience, which includes conducting 200 link audits in 2013, most reconsideration requests are turned around in 30 days or less. That said, it’s reasonable to conclude that 95 percent of all websites receiving a penalty don’t even bother to attempt a recovery. This guide is for the 5 percent of webmasters and business owners who are desperately seeking recovery.
The 5 Stages of Google Grief
Whenever a prospective client reaches out, the process invariably unfolds along the five stages of grief.
1. Denial
It begins with a notice like this:
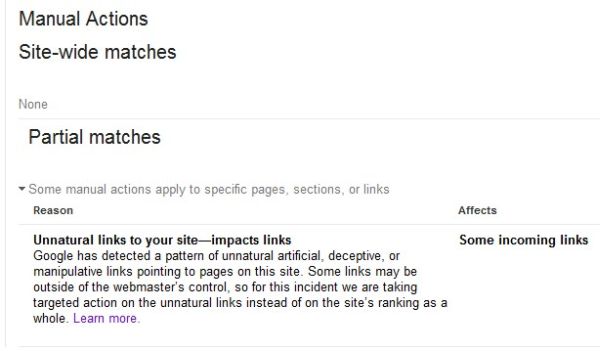
Or perhaps this, in Google Webmaster Tools:
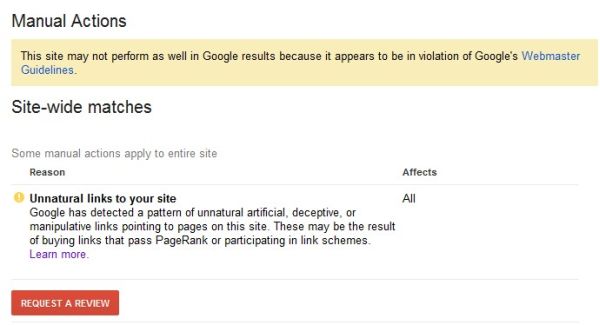
Your first reaction to this message is probably to deny the reality of the situation. People convince themselves that it must be a mistake. They can’t believe they’ve broken webmaster guidelines and their links are considered to be spam. This is a temporary response to the initial shock and fear.
2. Anger
As denial begins to fade, anxiety and fear emerge. People feel helpless – they aren’t sure what to do. They become angry. Anger is aimed at Google and SEO partners. Anger may also be directed at competitors with even worse backlink profiles.
3. Bargaining
This is a normal reaction to feeling helpless and vulnerable. There is a strong desire to regain control.
4. Depression
Depression is related to the practical implications of the penalty. Sadness and regret are pervasive. People worry about the loss of revenues. They worry about providing for others that depend on them. People need assurance that a penalty revocation is possible.
5. Acceptance
This phase is marked by calm. This is not a period of happiness, but rather a time to regroup and move forward.
Steps to Recovery
It’s time to put the recovery plan into action.
1. Don’t Rush
Now that you have an understanding of the emotional rollercoaster that a manual penalty brings, you need to control those emotions. Fight the urge to do a quick reconsideration request within hour or days of a penalty. Those who don’t take the proper time and steps to remove unnatural links get a notice like the following:
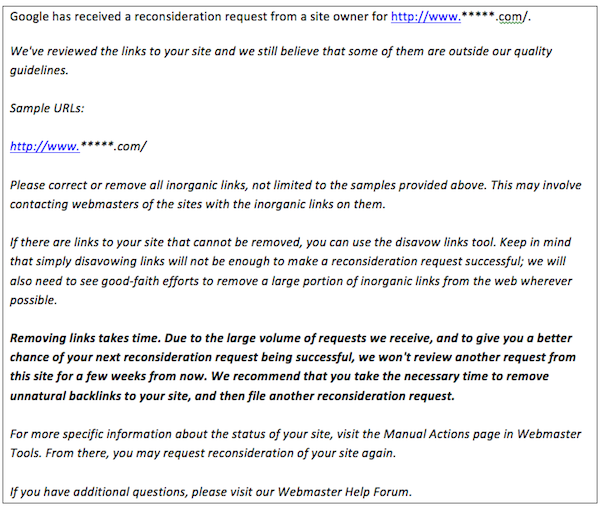
2. Conduct a Link Audit
Start with the links in Google Webmaster Tools. In most cases, (but not all) the key to recovery will lie there.
Navigate to Search traffic > Links to your Site > who links the most – More > Download Latest Links
Based upon the feedback that we receive from Google, primarily sample links provided when a reconsideration request is first denied, we have developed the following link classifications and related actions:
- Links not Found: No link could be located on the page. Disavow. An argument could be made that if the link isn’t there, there’s no need to disavow it. My view is that it’s better to be safe than sorry and prevent damage from a spam link that might somehow reappear.
- Page Offline: Links on pages that are no longer on the web. Disavow using the same rationale as above.
- SPAM TLDs: This one has geographic implications, but the most common one that we come across is .ru. It’s very rare that an English website would naturally attract massive numbers of links from Russia. Disavow – the likelihood of getting a response to a removal request is nil.
- Scrapers: Links on spam sites that copy their content from other websites. Disavow – the likelihood of getting a response to a removal request is almost nil.
- Spam Pages: Links on pages with PPC (Porn, Pills, Casinos), spam blog comments, spam forum signatures, or otherwise unrelated or spammy. Disavow or Request Removal – The likelihood of getting a response to a removal will be proportionate to the “quality” of the website. Use your judgment.
- Domain 0, G: As long as Google keeps updating it, we’re using PageRank as an audit metric. If a link is on a gray bar page and the domain is PR0, unless the domain is new and related. Disavow or Request Removal.
- Exact Match Anchor Text Manipulative: Exact match anchor text links built for the purpose of manipulating PageRank. These are the links that normally cause the biggest problems. Request removal.
- Penalized Domains: Links pointing to your site that reside on a website that has been penalized algorithmically or manually. Request removal.
- Link Network: Multiple links pointing to your site from websites that are part of a link network. Request removal.
- Partner Sites: If you have a network of websites that are related, unique, and interlinked, use a nofollow attribute to avoid the appearance of a doorway page or link manipulation. Keep, once nofollowed. If you have multiple websites in the same niche, all selling the same products, pick the best and retire the rest.
- Social Media links: Most are nofollowed. Keep.
- Nofollow Links: Keep.
- Natural, organic links: Keep.
For details on the best way to identify these link types, please read How to Conduct a Link Audit.
3. Set Up a Dedicated Google Drive Account
Once you’ve identified the bad links, it’s time to drop them into a Google Drive spreadsheet with the following information:
- Link From URL: URL where the link resides.
- Link to URL: The page (URL) on your website the link points to.
- Email contact: For the “Link From” website.
- First Link Removal Request: Insert date of removal request.
- Second Link Removal Request: Insert date of removal request (One week after first request).
- Third Link Removal Request: Insert date of removal request (One week after second request).
- Link Status: Live or removed.
Keep meticulous records on this spreadsheet. This is the supporting documentation that you will be submitting with your reconsideration request to prove to Google that you have made a serious effort to resolve the problem.
4. Request Link Removals
There is a growing level of link removal fatigue among webmasters. Some have gone so far as to add email filters that send link removal requests directly to the spam folder.
I would love to see a stat regarding the number of “please add my link” requests vs. “please remove my link” emails that are sent out every day. At the current rate of penalty, the lines just may cross at some point.
In order to break the link removal request fatigue, it’s extremely important to write an effective link removal request. Keep it short and specific:
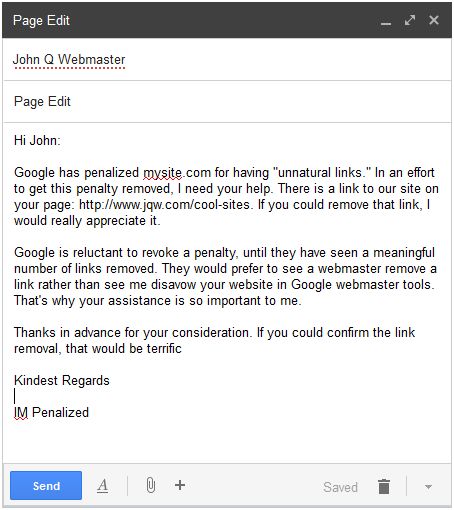
By including unique details like the webmaster’s name and the URL where the link is placed, you are more likely to be perceived as human. You also make it easy for the webmaster to find and remove the link. I’ve seen some backlash online regarding link removal “disavow threats”, so we have toned this way down as compared to our early outreach.
What is the Best Email Approach?
Some prefer to use an email address associated with the penalized website: [email protected]. The thought is that a domain based email provides maximum credibility. My concern with this approach is getting a domain’s email torched by having it marked as spam.
My preferred method is to use Gmail from the Dedicated Account created for the link removal campaign. A cc to [email protected] seems to add sufficient credibility. By having all of the email outreach documented there, it’s easy to share with Google. Using Gmail canned responses further adds to the efficiency.
Start Emailing
Using the information on your Google Drive spreadsheet, add the personalized details to your emails and begin sending. Record the date of every link removal request sent. In some cases you will need to submit a web form in lieu of an email – remember to also record these form submission dates on the spreadsheet.
Record every link removal and remember to stop emailing webmasters after links are removed. After five days have passed, send a “second notice”, to those who failed to respond the first time.
Once again, record every link removed and stop emailing those webmasters. After five more days, send a “final” notice to any holdouts.
The last step is to wait five more days to allow responses to the third round of emails. Any links still remaining, after three removal requests, will be added to the “Disavow Links tool.”
Yes, this is a lot of work, but failure to show a good faith effort to resolve the problem will only extend your penalty time.
5. Disavow Links and Submit a Reconsideration Request
Log into Google Webmaster Tools, go to the Disavow tool, and select your domain.

Clicking Disavow Links prompts a menu asking you for a file containing the links you want to disavow. This file should include all of the links initially targeted for disavow plus any links targeted for removal, that were not. Upload the file and you’re done.
Now it’s time to file a reconsideration request. When filing your request, here are some key points to consider:
- Be specific: Carefully review Google’s webmaster guidelines.
According to Google, the following activities are link scheming:
- Buying or selling links that pass PageRank.
- Using automated programs or services to create links to your site.
- Linking to a site for the sole purpose of getting a link back.
- Building a link network for the purpose of linking.
- Large-scale article marketing or guest posting using keyword-rich anchor text.
- Buying advertorials or articles that include links that pass PageRank.
- Creating and distributing press releases with optimized anchor text.
Disclose all activities that you were engaged in that fell outside of the guidelines. Explain in detail the actions taken to get links removed. Let Google know this is fully documented in Google Drive – share your drive credentials.
- Confess Everything: You must be completely honest and upfront. You need to provide as many details and specifics as possible. A simple: “My site now adheres to the guidelines.” won’t fly. If your link building foundation is built on SENuke and blog networks, then say so. You won’t be telling Google anything they don’t already know. If you fail to disclose a paid link you think Google “can’t detect,” then you’re just wasting precious time and burning trust with Google.
- Accept Responsibility, Promise it Will Never Happen Again: Explain what you’re doing differently now and why it will never happen again (e.g., you fired the person who was doing your SEO or you’ve changed your policy). If the spam team doesn’t get the sense that you have made a serious effort to clean up your backlink profile, they won’t believe that you are serious about change.
- Being a Huge AdWords Client Won’t Help: The spam team couldn’t care any less about your PPC budget. To them, it’s irrelevant.
Key Takeaway: Penalty Revocation Equals Permanent Probation
Google penalties get more severe for repeat offenders. After being penalized you have no choice but to strictly adhere to the Google Webmaster Guidelines. This will be a hard pill for many to swallow as the revocation of a penalty is just the first step in what is likely to be a long recovery period to regain traffic and rankings.






